Diagnosis
- Diagnostic Criteria
- DSM IV (1994 à2013)
- DSM 5 (2013 onwards)
- Diagnostic Tools
- INCLEN
- AIIMS Modified INDT-ASD Tool
DSM-IV

DSM-5
- DSM 5 (2013)
- A single diagnosis replaces the sub-divisions
- Diagnosis based on 2 areas
- Deficits in social communication and Fixated interests
- Repetitive behavior
- Restriction of onset age loosened from 3years to “early developmental period”
- New severity ranking
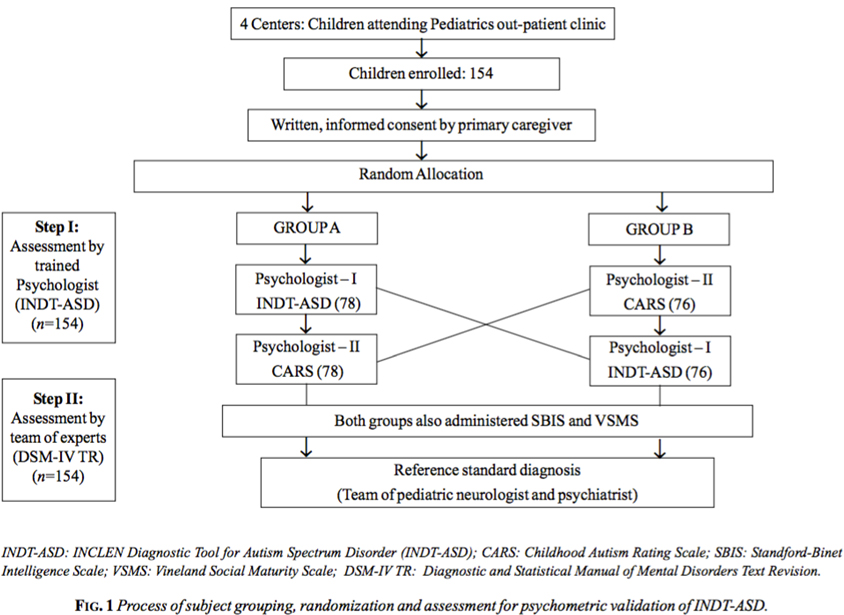
Development of INDT ASD Tool for Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
| INVESTIGATORS of INCLEN NDD PROJECT |
Dr. Narendra Arora (Project Leader)
Dr. MKC Nair (Principal Investigator)
Dr. Jennifer Pinto-Martin (Co-PI)
Dr. Donald Silberberg (Co-PI)
Dr Sheffali Gulati (Network Coordinator) |
INCLEN STUDY GROUP |
| Arun Singh |
J.C Gupta |
Poonam Natrajan |
Sunil Karande |
| A.K Niswade |
Archisman Mohapatra |
Rajesh Sagar |
Sanjay Rai |
| Alok Thakkar |
K.K Handa |
Rakesh Kumar |
Satinder Aneja |
| Arti Maria |
Maureen Durkin |
Ravindra Pandey |
Savita Sapra |
| Atul Prasad |
Monika Juneja |
Rohit Saxena |
Sharmila Mukherjee |
| B.C Das |
Madhuri Kulkarni |
Ritu Juneja |
Sunanda K |
| Bhadresh Vyas |
Muneer Massodi |
Rashmi Kumar |
Tanuj Dada |
| Devender mishra |
Manju Mehta |
Rashna das |
T.D Sharma |
| Faruque Ahmed |
Nandita Babu |
Rema Devi |
Veena Kalra |
| Gouri Dewan |
Nidhi Singhal |
Sandeep Bavdekar |
Vijay Chandra |
| Gautam Bir Singh |
Paul Russell |
Santosh Mohanty |
Vinod Bhutani |
| GVS Murthy |
Praveen Suman mehta |
Saradha Suresh |
Vinod Aggarwal |
| Harikumaran Nair |
Poma Tadu |
Sujatha Thyagu |
Zia Chaudhary |
| Abhishek Singh |
Abhimanyu Singh Chauhan |
Shobha Sharma |
Vaishali Deshmukh |
Research Paper

Indian Padiatrics
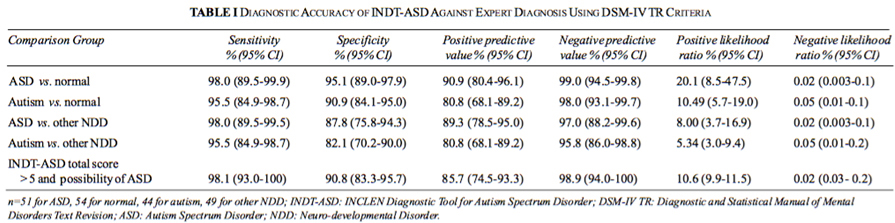
INDT-ASD Diagnostic Tool (DSM-IV based)
- The diagnostic accuracy [AUC=0.97 (0.93, 0.99); P<0.001]
- Sensitivity 98%, specificity 95%, PPV 91%, NPV 99%
- Merits:
- High diagnostic accuracy
- Adequate content validity
- Good internal consistency
- High criterion validity
- High to moderate convergent validity
- Easy to administer; no training required
- Concern:
- Use of DSM-IV as gold standard
- Lack of severity scoring

INCLEN Diagnostic Tool for Autism Spectrum Disorder (INDT-ASD): development and validation. Indian Pediatr. 2014 May;51(5):359–65.
Why Move From DSM-IV to DSM-5?
- DSM-5 provides a single umbrella diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder for:
- Autism
- Asperger syndrome
- Rett syndrome
- Childhood disintegrative disorder
- Pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS).
- Symptoms of autism spectrum disorder are specific (NOT pervasive) to impairment in social interaction and communication with presence of restrictive, repetitive behaviour.
- There are concerns of PDD-NOS being labelled as mild developmental disorder and Asperger as ‘odd’ behaviour.
- Overuse of PDD-NOS leads to diagnostic confusion and may contribute to epidemic of autism
- Symptoms of autism spectrum disorder are not salient among children with Rett syndrome
- Developmental regression in autism spectrum disorder has a wide range in timing and nature of loss of skills, hence precise existence of childhood disintegrative disorder has been challenged by many author worldwide.
- Literature has suggested that there is a considerable overlap between high functioning autism and Asperger syndrome questioning the need for separate category for the latter.
Development of AIIMS Modified INDT ASD Tool for Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Development and Validation of DSM-5 Based AIIMS Modified INDT ASD Tool
- Aim of the study was to develop and validate AIIMS modified INDT-ASD tool for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) against gold standard DSM 5 criteria for diagnosis and categorization of severity of ASD in children aged 1-14 years
Conducted in Child Neurology Division, Department of Pediatrics, AIIMS, Delhi
(Prof Sheffali Gulati) in collabartion with INCLEN group
Development of AIIMS Modified INDT-ASD Tool
- A team of national experts reviewed the pool of questions (Focused group discussion) in the new tool
- Pediatric neurologist
- Clinical psychologist
- Child psychiatrist
- Pool of items were selected by investigator using modified Delphi method
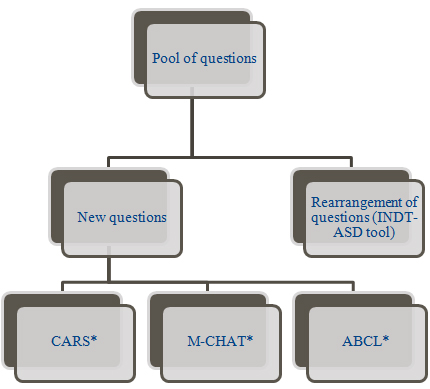
*CARS: Childhood autism rating scale
*M-CHAT: Modified checklist for autism
*ABCL: Autism Behaviour Checklist
AIIMS Modified INDT ASD Tool for ASD
- Response was marked as “yes”, “no” and “unsure”
- “unsure” was considered “no” for statistical purpose
- Combination of question and observation
- Each question has been labelled as autistic or non autistic response
- Time taken: 25-30 min
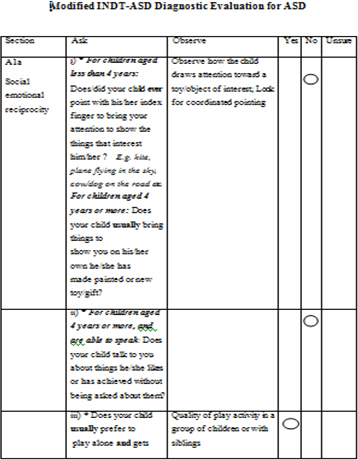
AIIMS Modified INDT ASD Tool
| AIIMS modified INDT ASD tool |
| DSM-5 |
Section A |
Number of items/questions |
| Social communication and interaction |
Social emotional reciprocity |
8 |
| Non verbal communication |
4 |
| Relationships |
3 |
| Restricted, repetitive pattern of behaviour, interest and activity |
Stereotyped movement or speech |
7 |
| Routines |
1 |
| Fixed interests |
1 |
| Sensory symptoms |
4 |
|
Total number of items |
28 |
|
Section B |
|
| Analysis of section A |
Summary of assessment |
9 |

Conclusion
- ASD diagnosis based on DSM 5
- Tools available
- INDT-ASD Tool
- AIIMS Modified INDT-ASD Tool
Thank You









