Outline of Presentation
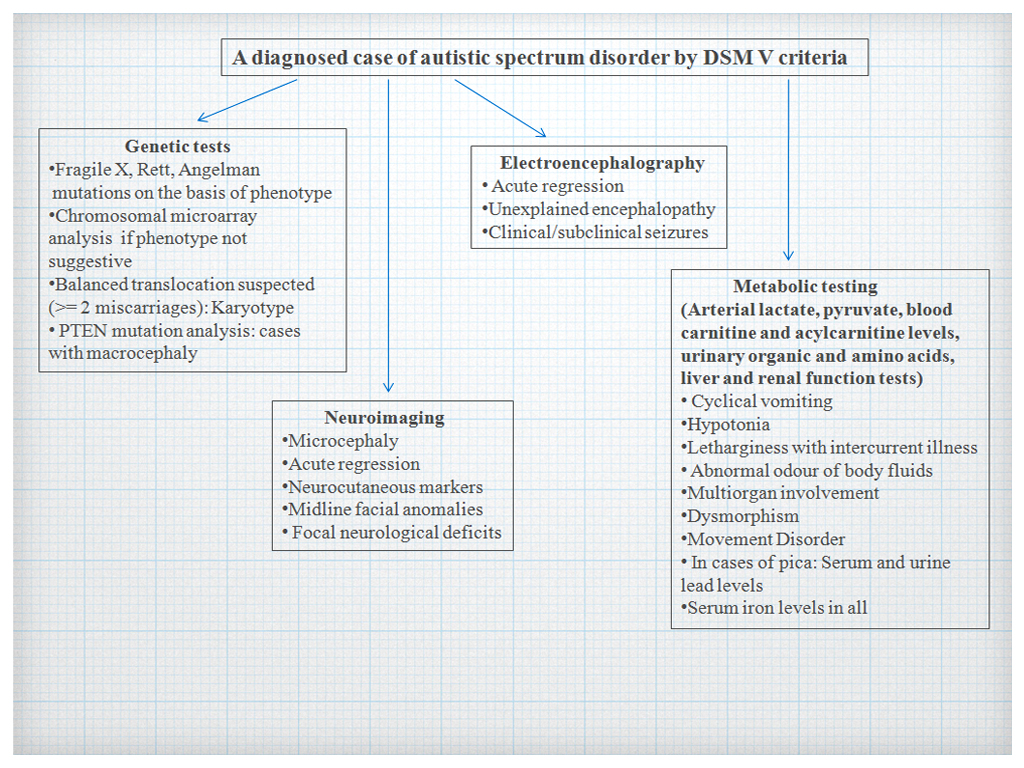
- Genetic investigations
- Neurometabolic testing
- Neuroimaging
- EEG
- Other tests
Genetic Counselling
- Multifactorial inheritance
- RR in siblings - 7% if the affected child is a girl
- RR in siblings - 4% if the affected child is a boy
- If a second child has autism, RR of 25–35%
- 2–3% of families have more than one affected children
Genetic Testing
Yield: 30-40%
- DNA testing
- Karyotype
- Chromosomal Microarray
- Next Generation Sequencing
DNA Testing
- Monogenic genetic syndromes(Upto 10%)
- Fragile X syndrome
- Tuberous Sclerosis
- Rett syndrome
- First tier: Molecular Fragile X screening
- Next: Direct gene analysis/ MLPA for deletion or duplication
- PTEN mutations: If macrocephaly
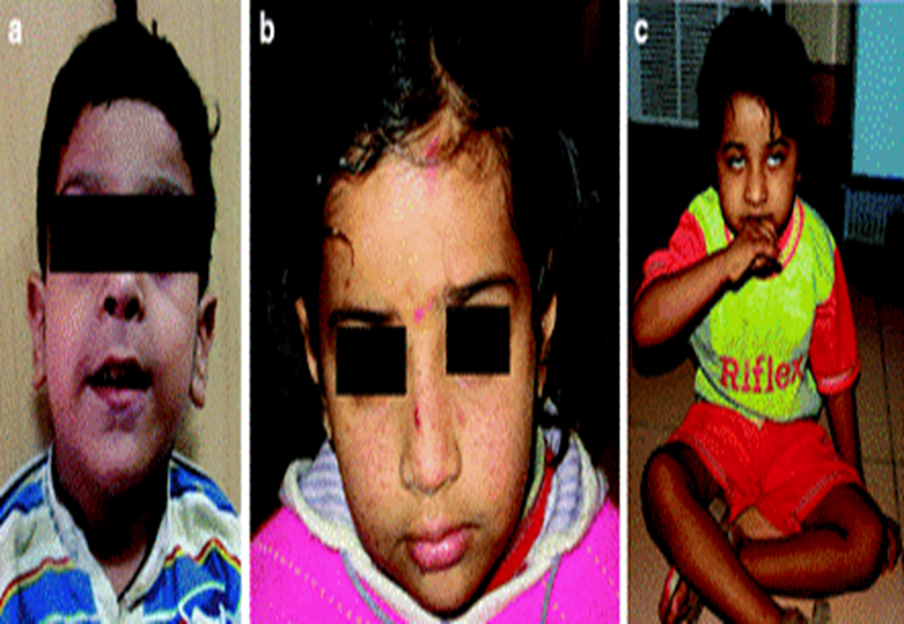
Courtesy: Division of Genetics, AIIMS, New Delhi
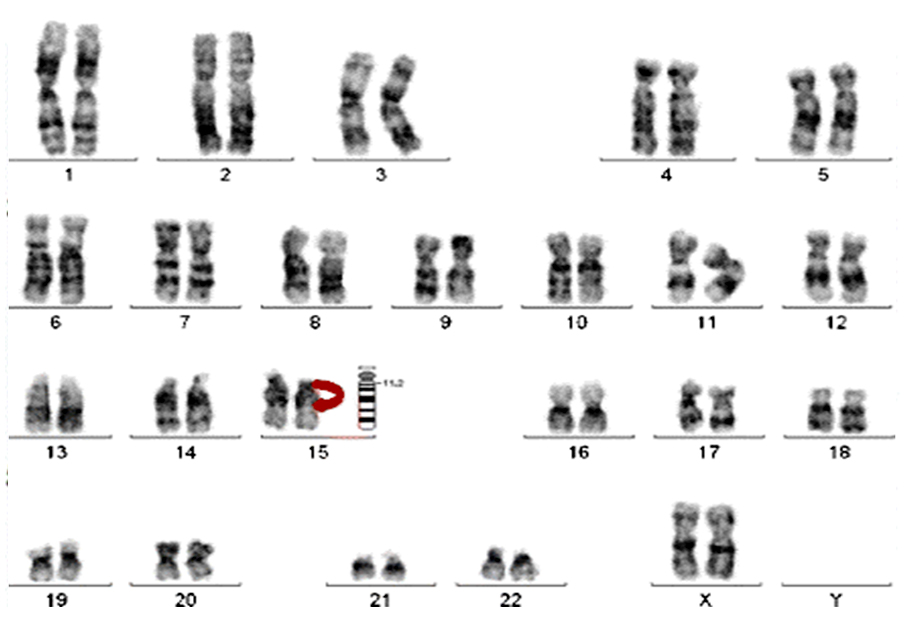
Karyotyping
- Upto 5 % (structural rearrangements, aneuploidy)
- Recurrent abortions
- For cytogenetically visible deletion
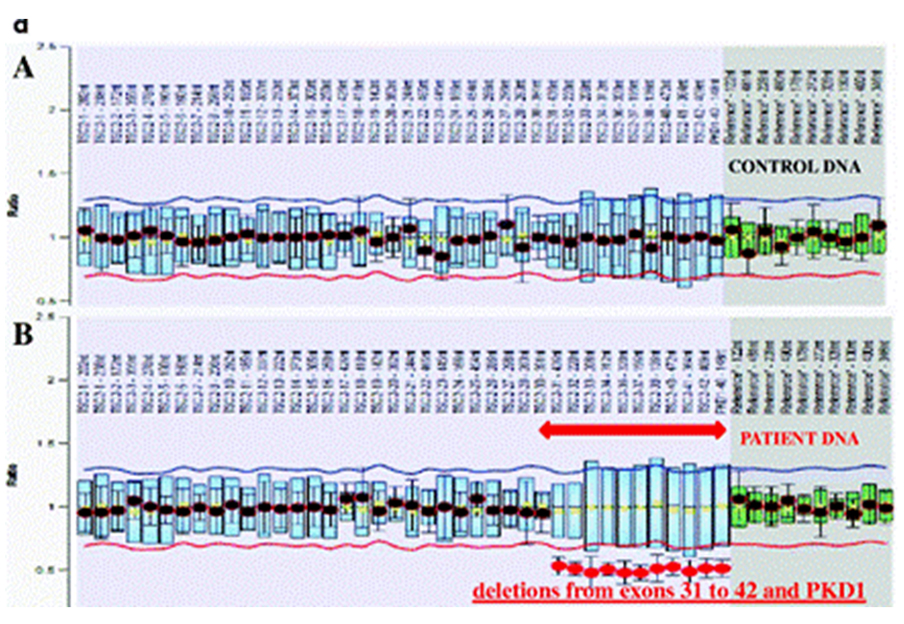
Courtesy: Division of Genetics, AIIMS, New Delhi
Array CGH
- For copy number variations (submicroscopic deletions, duplications, insetions)
- Increases the yield to upto 30%
Genet Med 2010
Next Generation Sequencing
- Single nucleotide variations (SNVs) and very small insertion or deletions
- Helpful in those with negative array CGH (increases yield by another 7 to10%)
- Trio studies help in detecting novel candidate genes and de novo mutations
Am J Hum Genet 2013;
Mol Autism 2014
Current Recommendation
- MLPA/ Karyotype: Recognisable Phenotype
- Array CGH
- NGS
Metabolic Screening
Indications (variable combination, yield <1%)
- Consanguinity
- Global regression
- Refractory epilepsy
- Movement disorder
- Skin rashes
- Focal neurological deficits
- Abnormal head size
- Lethargy
- Cyclical vomiting
- Multiorgan dysfunction
- Abnormal odour of bodyfluids
- Dysmorphism
DMCN 2016
Tests Recommended
- Tailored to individual cases
- Serum NH3
- Arterial lactate
- Urinary aminoacidogram
- Blood TMS
- Urine GCMS
- Urine MPS screen
- CSF sugar/lactate/neurotransmitters
DMCN 2013
Neuroimaging
- Focal neurological signs
- Dysmorphic features
- Neurocutaneous stigmata
- Abnormal head size (small/large)
- MRS: Metabolic disorders
AAP 2012
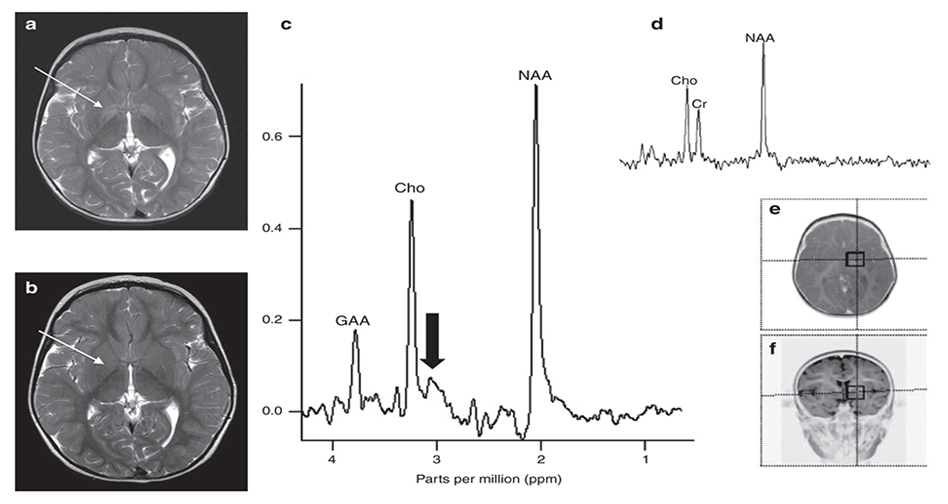
Tuberous Sclerosis
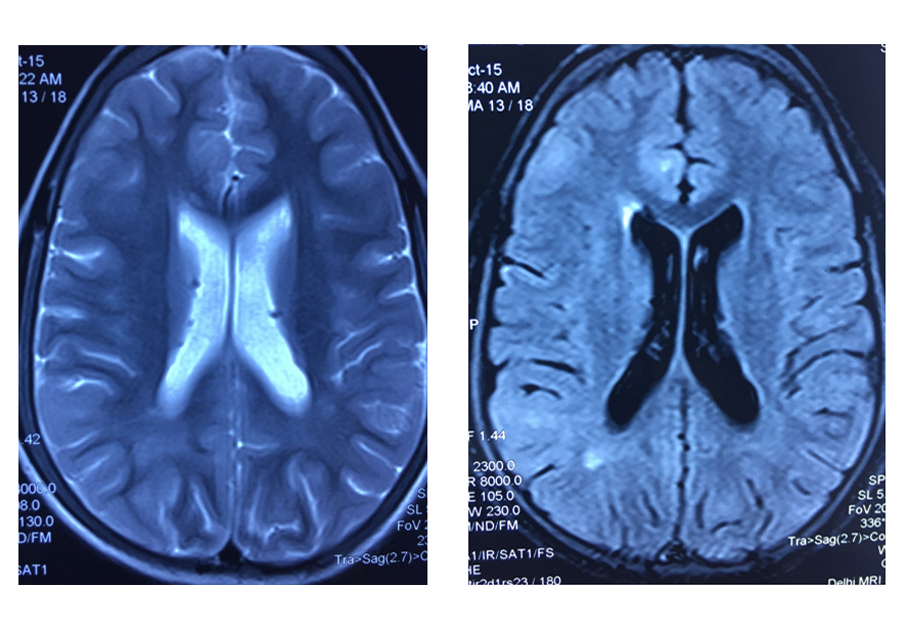
MRS: Cerebral Creatine Deficiency
Role of EEG
- Clinical seizures
- Unexplained encephalopathy or behavioral changes
- Cognitive Decline
AAP 2012
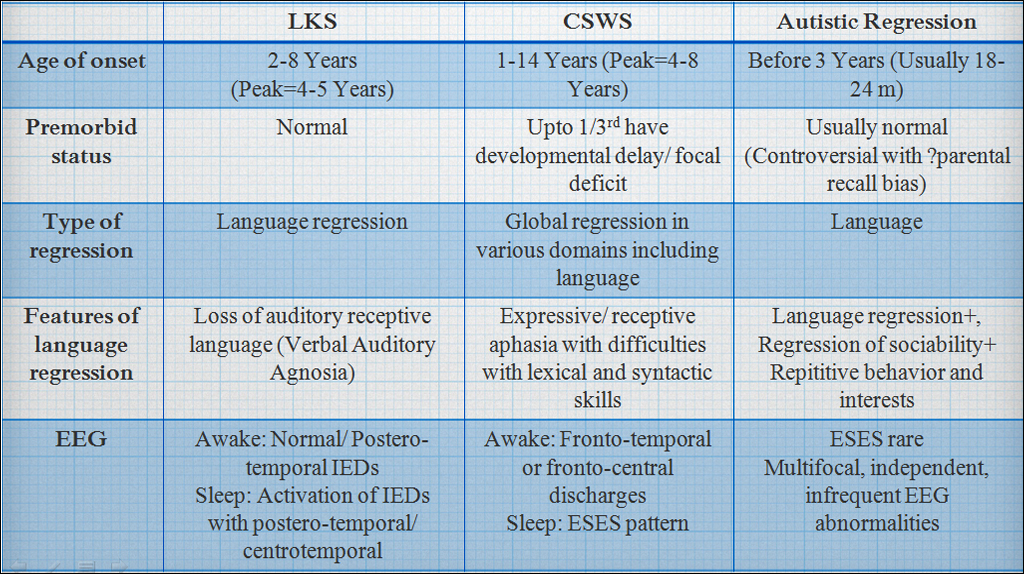
LKS
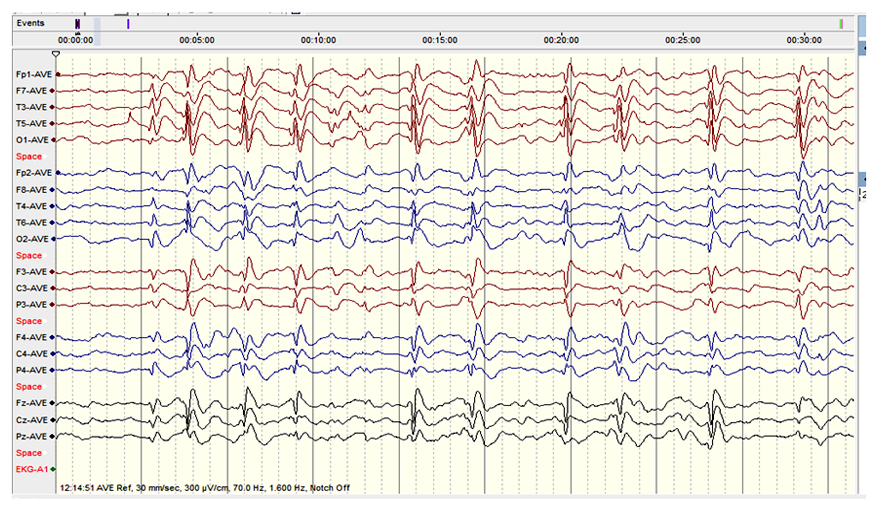
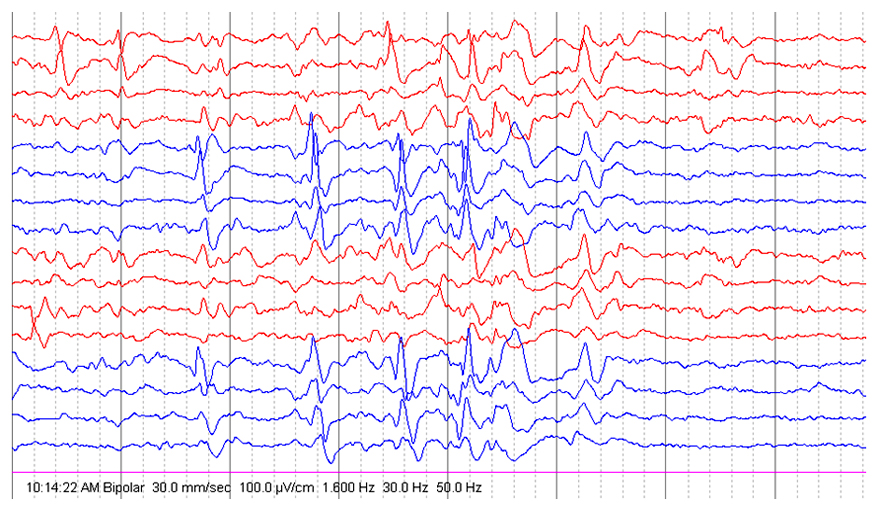
CSWS
Role of Other Tests
- Blood heavy metals (particularly in those with pica, serum lead levels)
- Serum Iron studies can be done in all
Not recommended
- Food allergy tests
- Hair mineral analysis
- Immunologic investigation
- Assay of vitamin B6 and magnesium levels
- Investigations to identify yeast over-growth in the gut
AAP 2012
Autism Mimics
- ESES: LKS and CSWS
- Autoimmune encephalitis: NMDAR
- Paraneoplastic
- Drugs induced behavioral problems
ESES
- Activation or potentiation of epileptiform discharges in sleep
- (Near)-continuous, bilateral, or occasionally lateralized slow spikes and waves
- Occurrence “during a significant proportion” of the non-REM sleep with a threshold ranging from 25% to 85%
- Original definition suggested >85%
- This criteria not required by ILAE
- Awake
- Most frequent locations of epileptiform discharges are
- Frontotemporal
- Centrotemporal
- In some cases, focal and generalized spike-wave complexes partially overlap
- Sleep
- Spiking becomes more frequent and ultimately generalized
- Frequently with a frontal or central maximum
ESES vs Autistic Regression
Autoimmune Encephalitis
- Anti NMDA receptor and Anti GAD encephalitis
- Expressive dysphasia and mutism are common clinical features in children and adults
- Result of NMDAR hypofunction
- A prodromal loss of social and communication skills can typify that of an autistic regression, particularly when presenting under age of 3 yrs
- Role of immunotherapy
Other Mimics (Case Reports)
- Paraneoplastic: Associated with ALPS
- Drug induced behavioral problems: associated with levetiracetam
Conclusion
- Yield of genetic testing in ASD is 30-40%
- Tiered approach is recommended for genetic testing
- Indication based investigation are recommended
- Role of EEG: in distinguishing autism mimics
Thank You








